News 2020

If the stacking structure of the “miracle material” COF is even slightly shifted, its properties change dramatically. This happens more often than assumed, as LMU-based chemists from the e-conversion cluster were able to demonstrate.
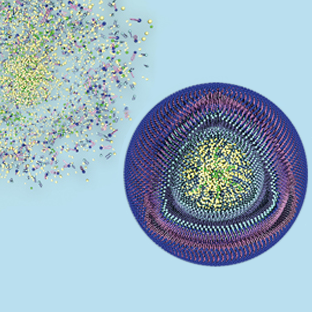
LMU researchers have developed a novel type of nanoparticle that efficiently and selectively kills cancer cells, thus opening up new therapeutic options for the treatment of tumors.

The pharmaceutical wholesaler PHOENIX honors innovative and outstanding work in pharmaceutical research with the PHOENIX Pharmaceutical Science Award. The prize was awarded for the 23rd time this year - endowed with a total of 40,000 euros.

For the 15th time, the Roemer Prize for outstanding achievements in biochemistry and chemistry was awarded this year.

Julian Stingele, Professor for Cellular Biochemistry at the LMU Gene Center since 2017, has been selected as EMBO Young Investigator.

A team led by LMU‘s Veit Hornung has shown that a protein found in skin cells recognizes a specific nucleic acid intermediate that is formed during virus replication. This recognition process subsequently induces a potent inflammatory response.

The synthesis and self-organization of biological macromolecules is essential for life on earth. LMU chemists now report the spontaneous emergence of complex ring-shaped macromolecules with low degrees of symmetry in the laboratory.

Sixteen LMU scholars and scientists are among the most influential authors in their specific fields, as the publication of the list of highly cited researchers 2020 shows. This ranking lists those researchers in the fields of the Natural Sciences, Social Sciences and Medicine whose publications are most frequently cited worldwide.
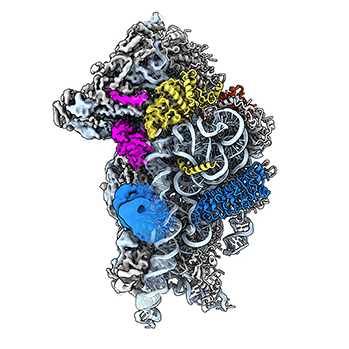
Ribosomes synthesize all the proteins in cells. Studies mainly done on yeast have revealed much about how ribosomes are put together, but an LMU team now reports that ribosome assembly in human cells requires factors that have no counterparts in simpler model organisms.

Scientists at LMU have identified the first mechanosensitive ion channel to be found in an intracellular vesicle system. It responds to concentration changes within the vesicle, and probably controls the initiation of immune reactions.
The heart can stably maintain blood flow – at rest or under stress – over a lifetime. Using a mouse model, an LMU team has now uncovered the role played by a specific class of ion channels in controlling the heart rate.

LMU researchers have developed photoresponsive derivatives of the anticancer drug Taxol, which allow light-based control of cytoskeleton dynamics in neurons. The agents can optically pattern cell division and may elucidate how Taxol acts.

Organic molecules formed the basis for the evolution of life. But how could inorganic precursors have given rise to them? LMU chemist Oliver Trapp now reports a reaction pathway in which minerals catalyze the formation of sugars in the absence of water.


Microswimmers are small particles that actively move in liquids. But they need a continuous energy supply. Thanks to a light charging mechanism co-developed by e-conversion members, microswimmers can now also move in the dark. This makes them interesting for medical applications.

Rare earth elements are vital for many modern technologies. Chemists at LMU have now shown that a cofactor found in a bacterial enzyme can selectively extract some of these metals from mixtures in an environmentally benign fashion.

Professor Veit Hornung has received the William B. Coley Award, endowed with a medal of honor and US $ 5,000, from the renowned US Cancer Research Institute (CRI) in New York.
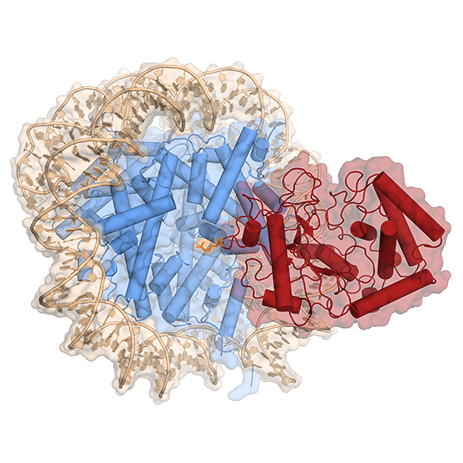
In higher organisms, detection of DNA in the cytoplasm triggers an immune reaction. The enzyme that senses ‘misplaced’ DNA is also found in the nucleus, but nuclear DNA has no such effect. LMU researchers now report why that is so.

Six early-career researchers have won ERC Starting Grants in conjunction with LMU, including Prof. Lena Daumann from the Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy.
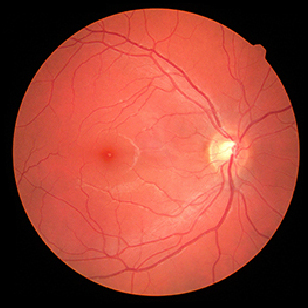
Retinitis pigmentosa is the most common form of hereditary blindness. Munich scientists have now used a gene therapy approach to compensate for the loss of defective genes in mice by specifically activating disused genes with a similar function.
Covalent cross-links between proteins and DNA are among the most hazardous types of DNA damage. LMU researchers have now characterized an enzyme that breaks such bonds, and elucidated how it specifically recognizes sites of damage.Covalent cross-links between proteins and DNA are among the most hazardous types of DNA damage. LMU researchers have now characterized an enzyme that breaks such bonds, and elucidated how it specifically recognizes sites of damage.
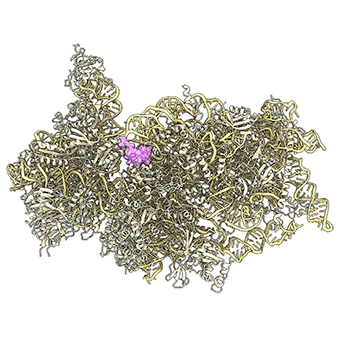
Researchers from Munich and Ulm have determined how the pandemic coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 inhibits the synthesis of proteins in infected cells and shown that it effectively disarms the body’s innate immune system.

Colored smoke is increasingly employed as an element of spectacle in a broad spectrum of public events. However, the chemicals used for this purpose give rise to toxic by-products. LMU chemists have now developed a safe alternative.

Last Monday, Bavarian Minister of Science Bernd Sibler visited the gene center and the chair for organic chemistry to find out about the current status of research on the novel virus SARS-CoV-2.


Lectures and internships for students are stopped!

An initial trial in patients indicates that a new genetic treatment for complete color blindness, developed by research groups based in Tübingen and Munich is safe. Preliminary evidence for its efficacy has also been obtained.
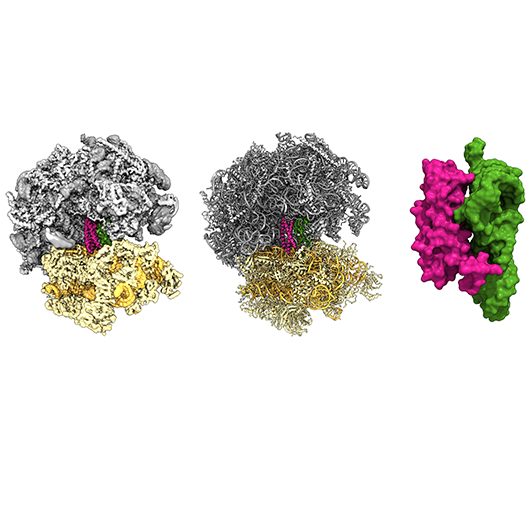
mRNAs program the synthesis of proteins in cells, and their functional lifetimes are dynamically regulated. LMU researchers have now shown why blueprints that are more difficult to decipher have shorter lifetimes than others.

LMU scientists have developed nanoparticles that release an overdose of iron ions in the cell depending on the pH. This could open up new therapeutic options for combating tumors, for example.

The European Research Council has awarded four of its coveted Advanced Grants to researchers at LMU. One price was awarded to Prof. Roland Beckmann of the Faculty of Chemistry.
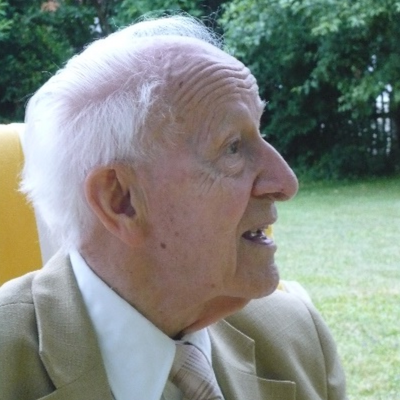

The faculty mourns the loss of Professor Dr. Dr. h.c. mult. Rolf Huisgen, who died on March 26, 2020, three months before his 100th birthday.
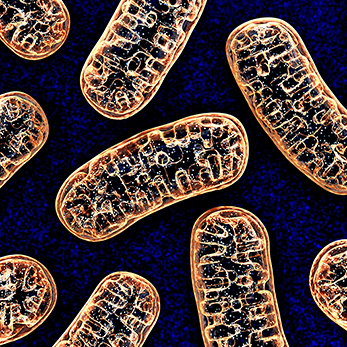
Mitochondria cannot autonomously cope with stress and must instead call on the cell for help. Molecular geneticists at LMU have identified the long-sought signaling pathway which enables the organelles to do so.
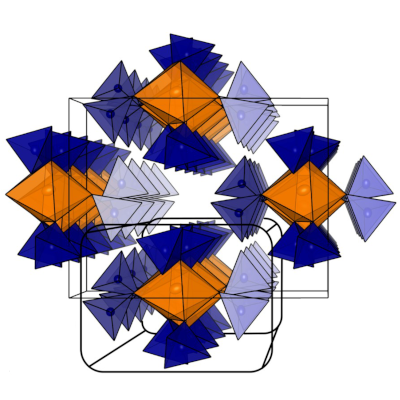
In the battery of the future, solids will replace the currently used electrolyte solutions. A team of scientists at LMU has now developed a series of new sodium ion conductors. The secret of the best material in the series lies in the exact mixing of the ingredients.

The LMUchemlab school laboratory of the Department of Chemistry under direction of Prof. Stefan Schwarzer, Department of Chemistry, Didactics, was awarded the LeLa Prize 2020 by the Federal Association of School Labs. The prize is donated by the BMBF.
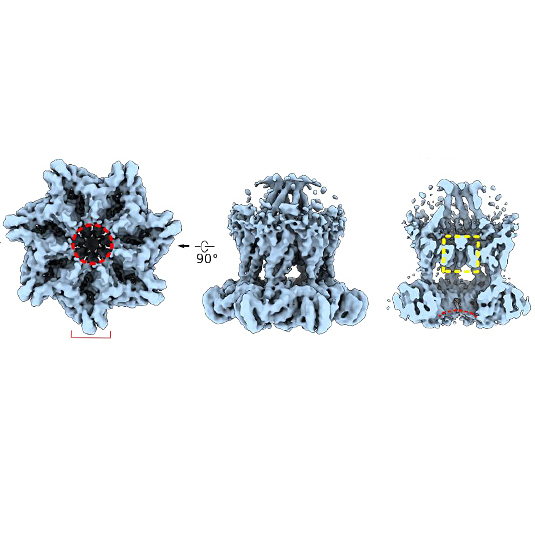
Bulky globular proteins require specialized transport systems for insertion into membranes. LMU researchers have determined the structure of such a system for the first time, and propose that it exploits the principle of the airlock.
A team of chemists at LMU has successfully coupled the directed motion of a light-activated molecular motor to a different chemical unit – thus taking an important step toward the realization of synthetic nanomachines.

Ivan Huc’s specialty might best be termed molecular mimicry. He designs and builds synthetic analogs of biomolecules that retain the essential features of their models, while exhibiting properties beyond those seen in nature.