Research

Figure 1. Correlation Analysis of the Reactions of Reference
Electrophiles with Neutral Carbon Nucleophiles.
Each correlation line corresponds to a p-nucleophile.
Seven of 23 benzhydrylium cations are depicted on the abscissa (ref. #180).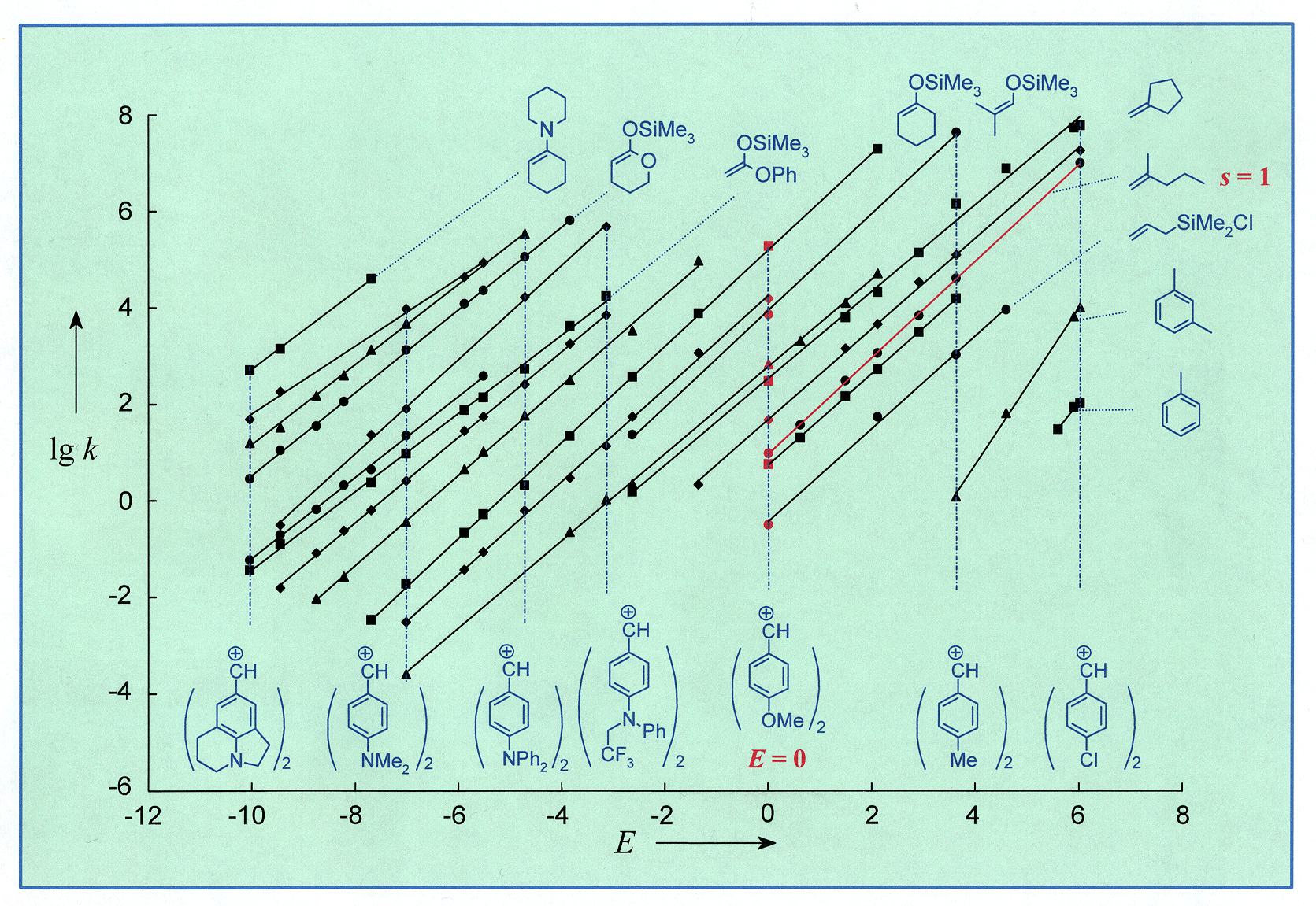
Figure 2. Correlation Lines for the Reactions of Benzhydryl Cations
and Quinone Methides with Neutral Nucleophiles and Carbanions.
Each correlation line coresponds to an electrophile (ref. #183).

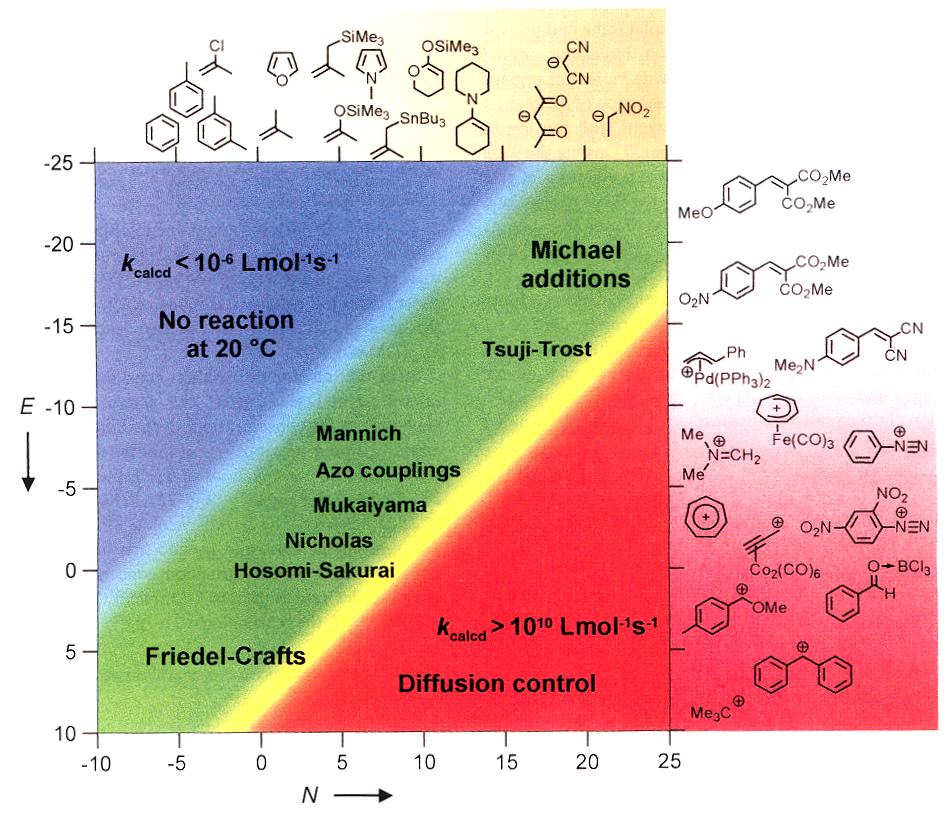
Figure 3. Reactivity parameters N and E of the
recommended reference nucleophiles and electrophiles (s in parentheses).
(PDF download,
117 kB)

Nucleophilicity Scales
Nucleophilicity parameters N and s are obtained by plotting log k(20°C) of the reactions of the corresponding nucleophile with several reference electrophiles towards the electrophilicity parameters E of the electrophiles (see Figure 4).
Figure 4.

Since s adopts similar values for nucleophiles
with similar reaction centers, nucleophilicity parameters N can
be derived from rate constants by using estimated values of s. The
results of such one-point calibrations are given in parentheses in Figure
5. Examples for determining N in this way are shown in publication
#191.
Figure 5. Reactivity parameters N and s for p-nucleophiles
(for the complete scheme from -5 < N <
14: PDF
download, 115 kB).
Electrophilicity Scales
The rate constants of the reactions of an electrophile with reference nucleophiles (which are depicted in the Figure 3) can be used for determining E according to the relationship
Though a single rate constant is in principle sufficient for determining E, the use of more than one rate constant is recommended in order to examine the validity of eq. (1). The results of one-point calibrations are marked by parentheses in the following Schemes.
Typical examples for evaluating E parameters
are given in publications #181
, #187,
and #188.
Figure 6. Electrophilicity parameters E of carbocationic electrophiles (PDF download, 103 kB).