The D5h Point Group
This point group contains the following symmetry operations:
E the identity operation
C5 a fivefold principal symmetry axis
5 * C2 five twofold symmetry axes orthogonal to the principal axis
σh a horizontal mirror plane intersecting the principal symmetry axis
5 * σv five vertical mirror planes aligned with the principal symmetry axis
S5 a fivefold improper rotation axis
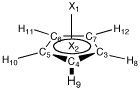
A simple example for a D5h symmetric molecule is the cyclopentadienyl anion
(C5H5-), here in its HF/6-31G(d) optimized structure:
#P RHF/6-31G(d) opt=(Z-Matrix,tight)
RHF/6-31G(d) opt min cyclopentadienyl anion D5h
-1 1
X1
X2 1 1.0
C3 2 r3 1 90.0
C4 2 r3 1 90.0 3 +72.0
C5 2 r3 1 90.0 4 +72.0
C6 2 r3 1 90.0 5 +72.0
C7 2 r3 1 90.0 6 +72.0
H8 2 r8 1 90.0 7 +72.0
H9 2 r8 1 90.0 8 +72.0
H10 2 r8 1 90.0 9 +72.0
H11 2 r8 1 90.0 10 +72.0
H12 2 r8 1 90.0 11 +72.0
r3=1.19285213
r8=2.27287212
|
| 
|
In this case the symmetry of the system is reflected in the Z-Matrix
through the use of identical variable names for carbon atoms C3 - C7
and for hydrogen atoms H8 - H12, through fixing the bond angles between
adjacent centers to 360/5 = 72 degrees, and through constraining all
atoms to the horizontal symmetry plane. This reduces the number of
independent structural variables from 24 (for an asymmetric, non-linear
molecule containing ten centers) to 2 and thus accelerates geometry
optimizations.
Molecular orbitals as well as harmonic vibrations (if calculated)
are labeled according to their symmetry properties as belonging to
one of the eight irreducible representations (
A1',
A2',
E1',
E2',
A1'',
A2'',
E1'',
E2'',
) of the D5h
point group.
last changes: 08.06.2006, HZ
questions & comments to: zipse@cup.uni-muenchen.de
